The haunting face of a man who lived 700 years ago
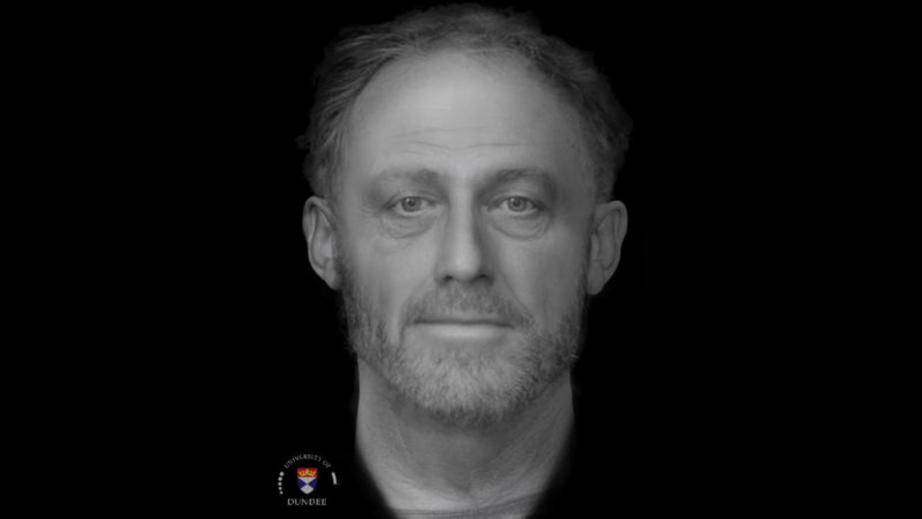

This may look like a photograph, but the highly realistic face staring back at you belongs to a man who died over 700 years ago. The researchers who performed this unbelievable facial reconstruction say their work is providing new details about the way ordinary people lived in medieval England.
This 13th-century man—dubbed “Context 958"—is one of approximately 400 complete burials found and excavated beneath the Old Divinity School of St. John’s College in Cambridge, England, between 2010 and 2012. Back during the medieval era, this spot was home to the Hospital of St. John, a charitable institution set up to care for the poor and sick in the community. For centuries, the dead were buried in a cemetery right out back.
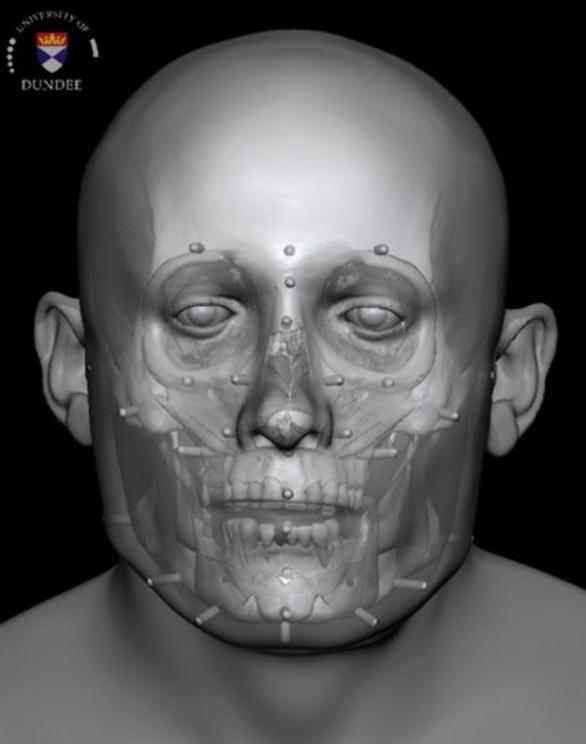
Facial reconstruction of Context 958. (Image credit: Dr. Chris Rynn, University of Dundee)
The reconstruction of Context 958 is part of a collaborative effort between Cambridge University’s Division of Archaeology and the University of Dundee’s Centre for Anatomy and Human Identification. The Wellcome Trust-funded project, called “After the plague: health and history in medieval Cambridge,” is an effort to catalogue and analyze the burials in as much depth and detail as possible.
Based on an exhaustive analysis of his remains and the burial site, here’s what we know about Context 958.
He was just slightly over 40 years old when he died. His skeleton showed signs of considerable wear-and-tear, so he likely lead a tough and hard working life. His tooth enamel stopped growing during two occasions in his youth, suggesting he likely lived through bouts of famine or sickness when he was young. The archaeologists found traces of blunt force trauma inflicted to the back of his head, which healed over before he died. The researchers aren’t sure what he did for a living, but they think he was a working-class person who specialized in some kind of trade.
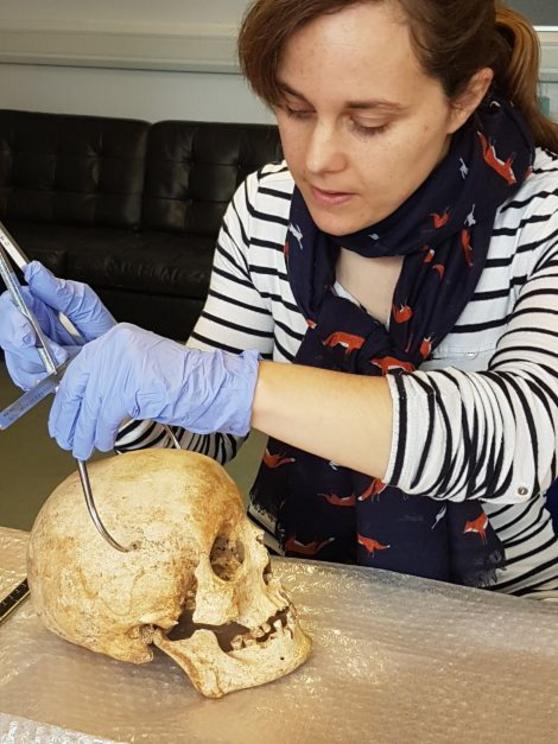

Dr. Sarah Inskip examines the skull of Context 958. (Image credit: Laure Bonner)
Context 958 ate a diverse diet rich in meat or fish, according to an analysis of weathering patterns on his teeth. His profession may have provided him with more access to such foods than the average person at the time. His presence at the charitable hospital suggests he fell on hard times, with no one to take care of him.
“Context 958 was probably an inmate of the Hospital of St John, a charitable institution which provided food and a place to live for a dozen or so indigent townspeople—some of whom were probably ill, some of whom were aged or poor and couldn’t live alone,” noted John Robb, a professor from Cambridge University’s Division of Archaeology, in a statement.
Strangely, he was buried face down, which is rare but not unheard of in medieval burials. Robb and his colleagues are fascinated by Context 958 and those like him. Their analysis shows what it was like to live as an ordinary poor person back then—warts and all.
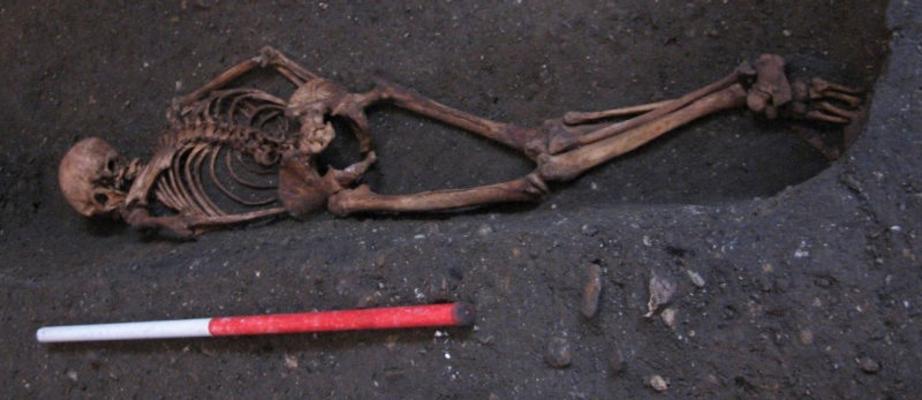

Context 958 was found buried face-down in the historic cemetery of St John’s. (Image credit: C. Cessford)
“Most historical records are about well-off people and especially their financial and legal transactions—the less money and property you had, the less likely anybody was to ever write down anything about you,” said Robb. “So skeletons like this are really our chance to learn about how the ordinary poor lived.”
Of course, facial reconstructions are only as good as the data they’re based on, in this case a highly-weathered skeleton. We can’t be completely certain that this is exactly what Context 958 looked like. But at the very least, it’s bringing his remains back to life. Work on other skeletons found at the site will continue, as the researchers are putting together a kind of biography of every individual studied. It’s a fitting tribute to regular folks whose lives would have otherwise been completely forgotten.

