Incredibly preserved 2,400-year-old Celtic warrior's shield made from tree bark is dug up in Leicestershire - the first ever found in Europe
- It has been dated by radiocarbon to the Iron Age between 395-255BC
- The shield was found in pieces but has been reconstructed and analysed
- It was stiffened with wooden straps and has a rim and wooden handles
- And shows signs of being painted and scored with red chequerboard decoration
An incredibly well-preserved shield made from tree bark may be the find of the century and revolutionise what is known about Celtic weaponry.
It is the first shield ever excavated in Europe to be made from bark and dated by archaeologists who found it in Leicestershire to be 2,400 years old.
All other shields previously unearthed on the continent were made from timber or metal.
The use of bark made it far lighter than the alternatives and would have allowed its wielder to move swiftly as they were not restricted by a cumbersome shield.
Analysis shows that it was stiffened with wooden straps and fitted with a rim and handle to make it easier to hold and use.
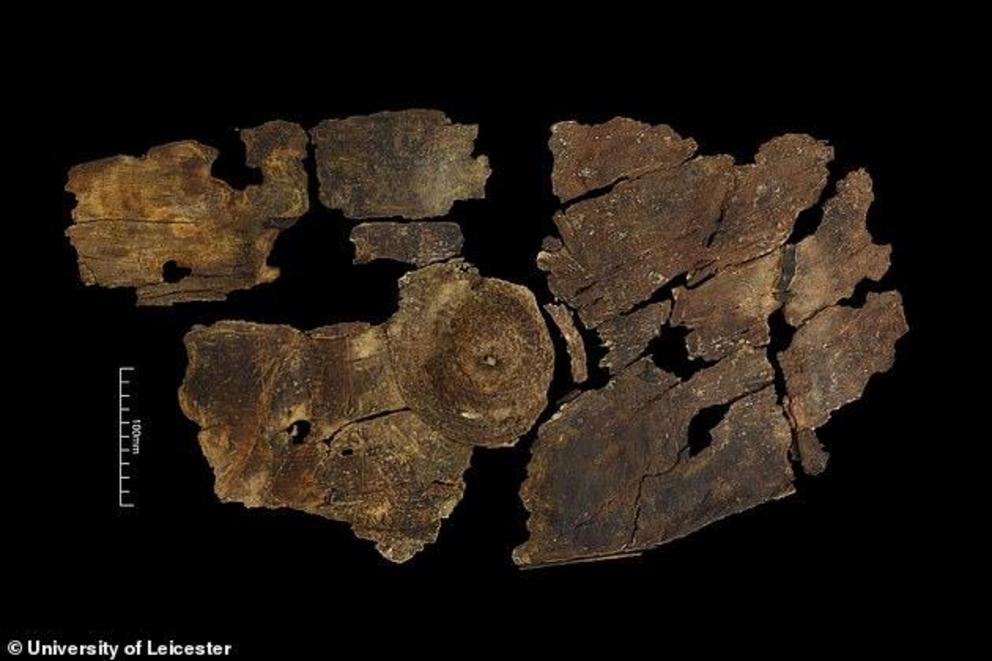 A prehistoric shield made of bark has been found has a stud (shown) on the centre of a shield formed from a willow core stitched together with a flat fibre of grass, rush or bast fibre. The image shows the front of the shield
A prehistoric shield made of bark has been found has a stud (shown) on the centre of a shield formed from a willow core stitched together with a flat fibre of grass, rush or bast fibre. The image shows the front of the shield
The shield was first discovered in 2015 south of Leicester on the Everards Meadows, buried deeply within the waterlogged soil of the excavation pit.
Known as the Enderby shield, it measured 26 x 15 inches (670 x 370mm) in the ground in a spot where archeologists think was once a livestock watering hole.
Speaking to MailOnline, Matt Beamish, project officer at the University of Leicester Archeology Services (ULAS), said: 'The shield was found "face down" in the ground and you could see part of the handle on the inside.'
Radiocarbon from the wooden pieces found has dated it to between 395 and 255 BC and researchers have made a modern copy using bark sliced from a tree.
Detailed analysis had showed that the bark came from either alder, willow, poplar, hazel or spindle tree and that the the outer layer of bark formed the inside of the shield.
Its consolidating straps were made of apple, pear, quince or hawthorn whilst the rim was a half-split hazel rod, say the researchers from University of York who found it.
The stud on the centre of the shield was made from a willow core stitched together with either a flat fibre of grass, rush or bast fibre.
'The handle made from willow roundwood, flattened at the end and notched, and fixed to the bark with twisted ties,' the archaeologists said.
The shield had been painted and scored in red chequerboard decoration using hematite based paint and was likely severely damaged from the pointed tips of spears nearby, before being cast into the ground.
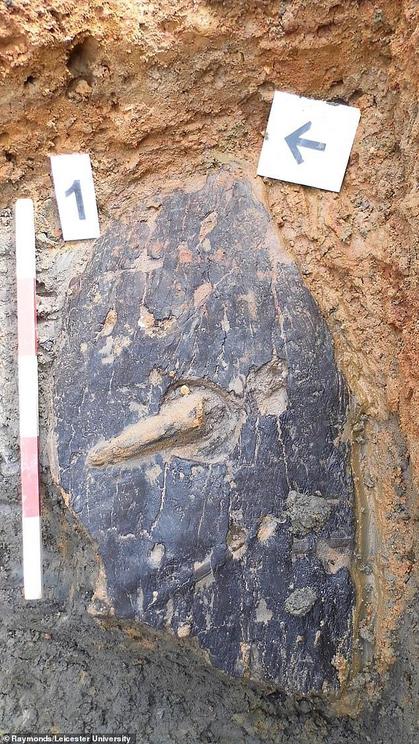 The object has been dated to 2,300 years ago and has all the signs of a working shield. The image shows the inside of the shield as it was found, 'face down' in the soil and part of the handle can be seen in the middle
The object has been dated to 2,300 years ago and has all the signs of a working shield. The image shows the inside of the shield as it was found, 'face down' in the soil and part of the handle can be seen in the middle
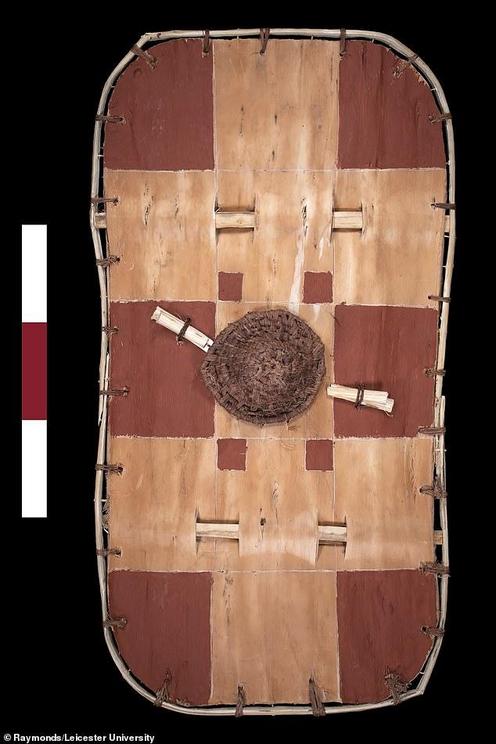 Analysis shows that it was stiffened with wooden straps and has a rim and handle. Shown is a reconstructed shield made by researchers from bark
Analysis shows that it was stiffened with wooden straps and has a rim and handle. Shown is a reconstructed shield made by researchers from bark
Researchers used an array of analytical techniques to understand the construction of the object, including CT scanning and 3D printing.
Dr Rachel Crellin, Lecturer in later Prehistory at the University of Leicester, explained why the find was so unique.
She added: 'Bark and basketry objects were probably commonplace in ancient Britain, but they seldom survive, so to be able to study this shield is a great privilege. It holds a rich store of information about Iron Age society and craft practices.
'Our initial thoughts that a bark shield would be too fragile for use in battle.
'Our experimental work showed that the shield could stand up to heavy impacts, including protecting from arrows.
'A bark shield, although not as strong as a solid wood or metal shield, is much lighter, allowing for speed and movement. '
 Known as the Enderby shield, it measured 26 x 15 inches (670 x 370mm) in the ground and was found in Everards Meadows where archeologists think was once a livestock watering hole (shown above)
Known as the Enderby shield, it measured 26 x 15 inches (670 x 370mm) in the ground and was found in Everards Meadows where archeologists think was once a livestock watering hole (shown above)
WHY WAS THE SHIELD MADE OF BARK?
There is good ethnographic evidence for shields made of bark in the southern hemisphere, from Australia, Borneo and the Philippines.
There has been little evidence for this in Europe, although Julius Caesar did record in his Commentarii De Bello Gallico (Commentaries on the Gallic War) that the Gauls had 'shields made of bark or interwoven wickers, which they hastily covered over with skins'.
The famous The Battersea Shield, dated to 350 BC-50 BC is made of several pieces of sheet bronze and is in fact a metal cover that was attached to the front of wooden shield.
Although a bark shield is not as strong as one made from wood or metal, use of bark would have made the weapon much lighter than metal or timber, and would have given soldiers more speed, archaeologists say.
According to the dig's website, barks shields may well have been common the Iron Age, but due to the lack of wood preservation and the biased survival of metal, it is hard to find evidence.
The shield is first of its kind to have been found in Europe, although there is evidence for bark shields in the southern hemisphere, from Australia, Borneo and the Philippines.
The famous The Battersea Shield, dated to 350 BC-50 BC is made of several pieces of sheet bronze and is in fact a metal cover that was attached to the front of wooden shield.
Michael Bamforth, project manager at the Department of Archeology at the University of York said: 'Initially we didn't think bark could be strong enough to use as a shield to defend against spears and swords and we wondered if it could be for ceremonial use.
'It was only through experimentation that we realised it could be tough enough to protect against blows from metal weapons.
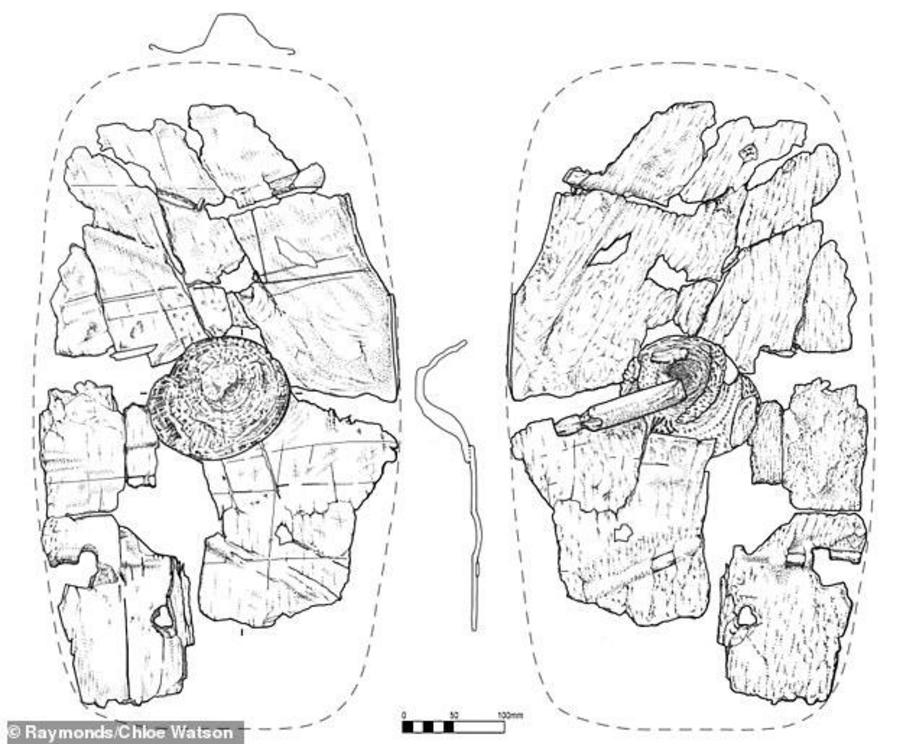 The use of bark would have made the weapon much lighter than metal or timber, and would have given soldiers more speed, archaeologists say. The image shows a the front (left) and back (right) of the piecestha make up the shield, with the latter showing th
The use of bark would have made the weapon much lighter than metal or timber, and would have given soldiers more speed, archaeologists say. The image shows a the front (left) and back (right) of the piecestha make up the shield, with the latter showing th
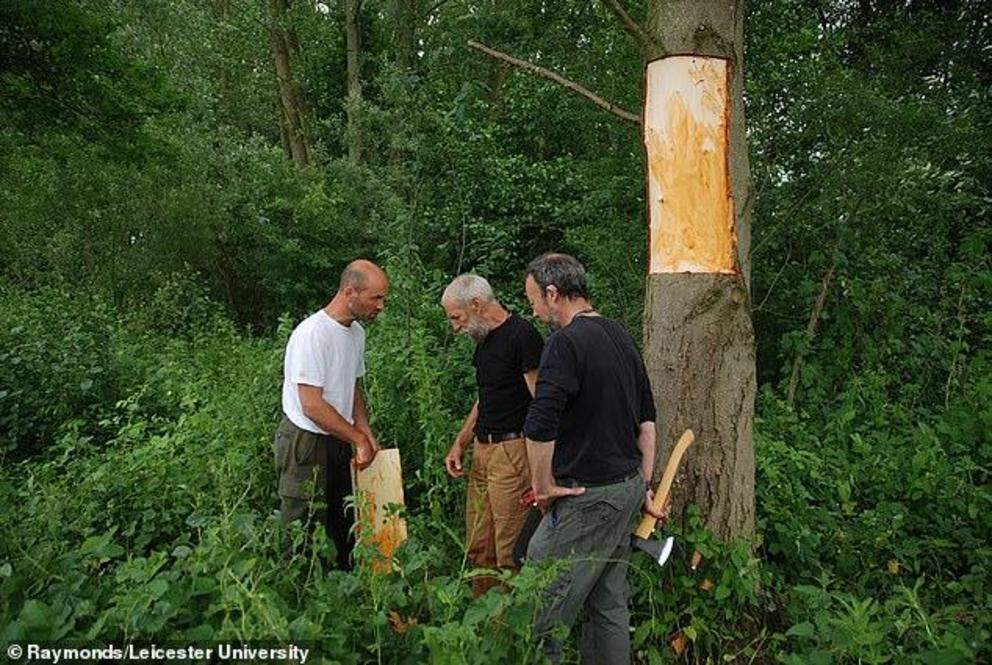 The shield was found south of Leicester on the Everards Meadows, buried deeply within the waterlogged soil of the excavation pit. The image shows researchers from Leicester University trying to reconstruct the shield
The shield was found south of Leicester on the Everards Meadows, buried deeply within the waterlogged soil of the excavation pit. The image shows researchers from Leicester University trying to reconstruct the shield
Although a bark shield is not as strong as one made from wood or metal, it would be much lighter allowing the user much more freedom of movement.'
Further analysis is planned to help understand if this occurred in battle or as an act of ritual destruction.
The shield has now been conserved by York Archaeological Trust and will be deposited with the British Museum on behalf of Everards of Leicestershire, who funded and supported the project.
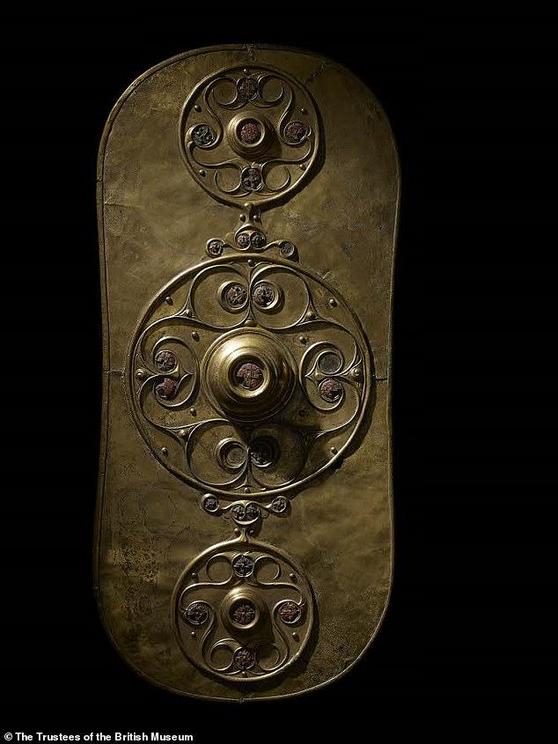 The famous The Battersea Shield, dated to 350 BC-50 BC is made of several pieces of sheet bronze and is in fact a metal cover that was attached to the front of wooden shield
The famous The Battersea Shield, dated to 350 BC-50 BC is made of several pieces of sheet bronze and is in fact a metal cover that was attached to the front of wooden shield
WHAT WAS CELTIC WEAPONRY?
The Celts made sophisticated and horrifying weaponry.
Some of the best Celtic art in Iron Age Britain was used to decorate killing machinery, particularly scabbards, sword hilts and shields.
The Eaton hoard, found on the edges of Norwich contains 145 bronze axes and spearheads dating from between 950BC and 750BC.
It showed a warring civilisation and a pretty advanced manufacturing that could turn out weapons on a mass production basis.
The Greeks and Romans considered the Celts to be wild barbarians with their horned helmets and gleaming, elaborately decorated shields, they fully intended to present as shocking a sight as possible.
Their weapons were not just for killing either, but for glittering display, to put the fear of God into the enemy, long before their weapons clashed.
The ‘Battersea shield’, found in the Thames at Battersea, South London, and thought to have been made between 350BC and 50BC is made of polished bronze, raised decoration and red glass inlay, it is thought to have been a ‘display shield’, raised aloft in flamboyant display to get the enemy quaking.
Celts were known to attack at top speed in massed charges during battle and just killing their enemies was not enough.
Evidence shows that they ripped the heads from their dead foes and strapping them to their belts or horses, a symbol of the strength they had taken from those they had vanquished.
Video can be accessed at source link below.
